What is National Public Procurement?
National Public Procurement refers to the process by which Government Organizations/Departments/PSUs/Autonomous Bodies/Various Government Aided Projects/Universities buy goods and services from the private traders and manufacturers. This Public Procurement requires to follow strict procedures in order to ensure that the purchase process is fair, efficient, transparent and minimizes the cost involved in completing the whole of the purchase cycle including on-site delivery and if required installation also.
Existing Challenges:
Given the scale and geographic spread of public procurement in India across Central and State Ministries, Departments and their affiliates, India’s public procurement landscape was marred by many inefficiencies, a few of which are listed below:
A. Limitations & Inefficiencies in procurement system
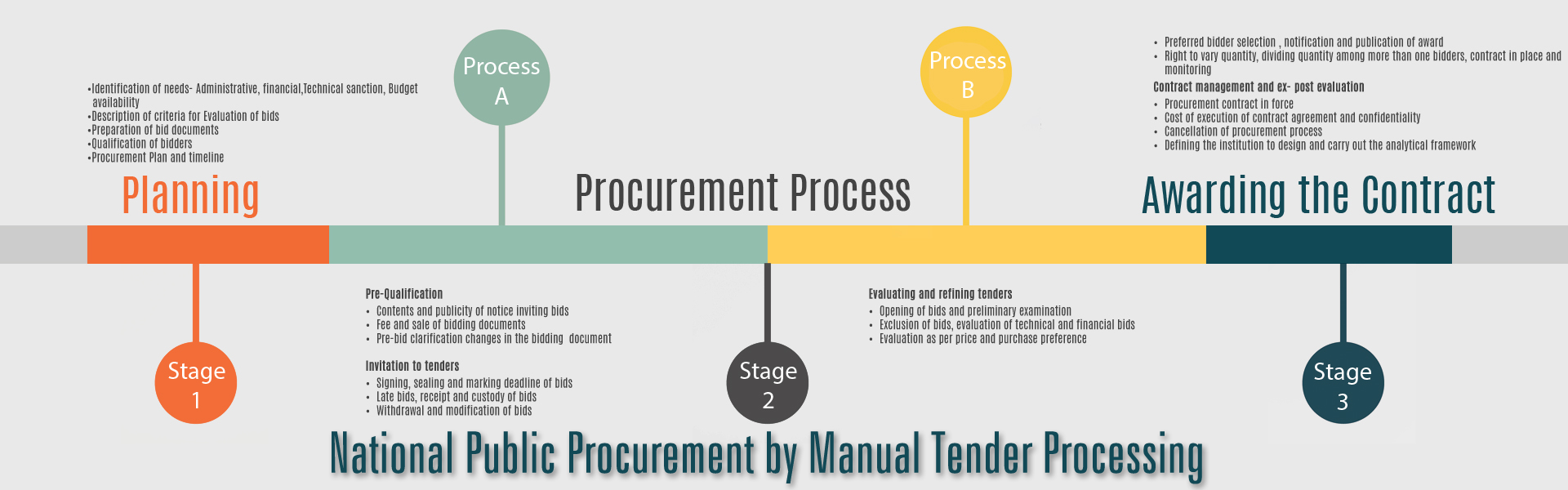
- Geographic coverage of standardized procurement limited to localized vendor base.
- Non-availability of granular data/ MIS on public procurement.
- Limited range of product categories under standardized rate contracts.
- Lack of price reasonability (either individually selected vendors OR prices locked for 1 year under rate contracts).
- Limited demand aggregation/ benchmarking across organizations to optimize for bulk purchases.
B. Time-Consuming & Heavily Manual Processes
- Admin overhead for buying organizations in terms of manpower & effort required.
- Time consuming, cumbersome registration & verification processes for sellers.
- Manual process inefficiencies such as offline payments processes.
- Manual rate negotiations resulting in opacity and possible cartel formation.
Complex policy landscape with potential for conflicts – Many purchase preference policies exist in India today at both Central & State level resulting in complicated decision making for buyers. While a private buyer can choose his purchasing strategy flexibly, the public sector had limited options to respond dynamically to anti-competitive behavior due to strict regulatory and legislative framework as well as detailed administrative procedures on multiple levels of government.
Introduction to Government e-Marketplace (GeM):
"GeM" is an online, end-to-end marketplace reform that provides an open, efficient & transparent solution for Public Procurement Process.
The platform was launched on August 9th, 2016 by Hon'ble Prime Minister, based on recommendations of the Group of Secretaries, who decided to set up a dedicated e-market for different goods & services to be procured by Government various state & central Organizations/Departments/PSUs.This meant transforming old paper driven DGS&D (Directorate General of Supplies and Disposals, Govt. of India) platform into a digital e-commerce portal called Government e-Marketplace (GeM). "GeM" aims to enhance transparency, efficiency and speed in public procurement. It provides the tools of e-bidding, reverse e-auction and demand aggregation to facilitate the government users achieve the best value for their money. At full scale of operations, the savings from the platform will have a significant impact on lowering the fiscal deficit of the country. With Government e-Marketplace "GeM", procurement of common use goods and services required by central and state government ministries, departments, public sector undertakings, autonomous institutions, organizations, and local bodies at the right price, right quality and right quantity in a transparent and efficient manner. Within less than three years since its implementation, about 290,000 sellers & service providers have signed up to this platform. They are selling more than 1,400,000 products to more than 39,000 buyers organization across Central and State Government Ministries, Departments and their affiliates.
Managed by GeM Special Purpose Vehicle, a 100% Government Owned, Section 8 Company under the Department of Commerce.
Since, inception GeM has been able to achieve significant scale in operations and has taken many strides towards optimizing the operations on the platform. It has already achieved a cumulative GMV of close to 400 bn ₹, and is expected to grow 10x over the next two years. In the long run, over next five to six years it is expected to achieve its potential GMV of ~ 9000 bn ₹ equivalent to 4-5% of India’s GDP. GeM Special Purpose Vehicle, is accountable for maintaining and developing the technology platform. The platform is presumed to have led to overall savings of up to 25 percent in government expenditure while enhancing transparency and efficiency in public procurement process. The GeM is strongly tied to the “Make In India” initiative, aimed at fostering the idea of producing with local manufacturers within India and Technology Development for Indian Languages (TDIL), a platform for citizen engagement (MyGOV).






Alteration of General Financial Rule(GFR) :
The Indian government amended the GFR (General Financial Rules), by Ministry of Finance by adding a new Rule No. 149 in the General Financial Rules (2017) and brought about a change in procurement directives, that mandated all organizations and departments under Government Organizations and other said departments to procure from GeM.
Systemetic Support & Added Value of MSME :
GeM provides the purchasers/buyers with an option to select only Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) & choose a seller from amongst them. This has helped buyers in significantly increasing share of MSME purchases in their overall procurement of goods and services. GeM officially encourages MSME sellers through special filters on the portal. GeM aims to help all the government officials in purchasing goods and services that are of commonly used products like: Desktop Computers, Laptops, Servers, Single Function Printer Multi-functional office printing equipments, Networking equipments, & also services like Annual Maintenance Contact (A.M.C.) for Desktop Computer/Laptop etc. among others.